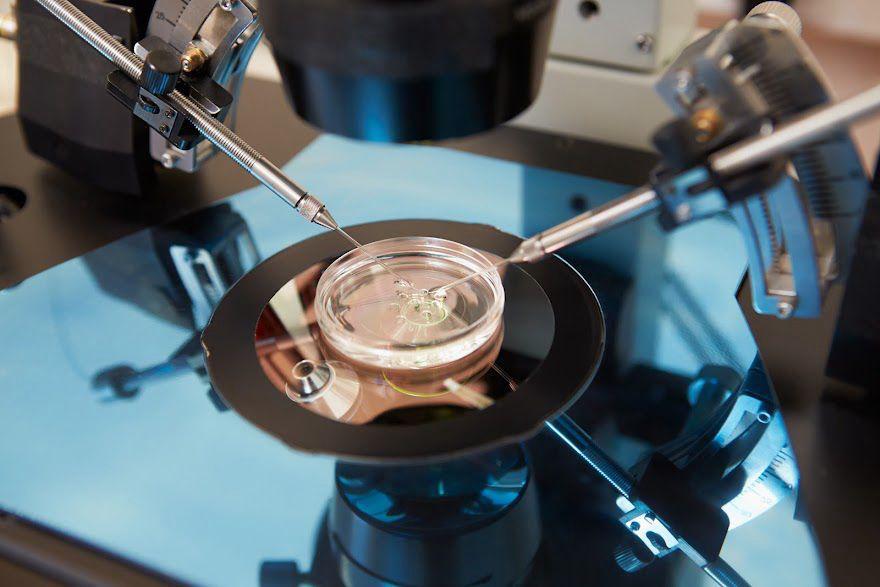
IUI Treatment & Precautions
Pregnancy typically occurs when sperm fertilizes an egg during intercourse. However, for couples facing challenges with natural conception, Intrauterine Insemination (IUI) offers a viable alternative. This procedure involves placing sperm directly into the uterus around the time of ovulation, increasing the chances of fertilization and pregnancy.
When Should You Consider IUI?
IUI is recommended in the following situations:
- Mild endometriosis
- PCOS/PCOD
- Irregular or absent ovulation
- Male factor infertility (low sperm count or motility)
- Genetic disorders
- Sexual dysfunction
- Cervical mucus problems
- Unexplained infertility
- STD/STI-related fertility concerns
- Age-related fertility decline
Timing is crucial. For women who ovulate naturally, ovulation is tracked via blood or urine tests, typically 12–16 days before the next period.
What If You Don’t Ovulate Naturally?
In such cases, ovulation needs to be medically induced:
- Fertility Medications – Tablets or injections to stimulate egg development
- Monitoring – Vaginal ultrasounds to track follicular growth
- Trigger Shot – A hormone injection to release the matured egg
Stages of the IUI Procedure
- Cycle Day 2–5: Baseline transvaginal ultrasound
- Ovulation Induction: Hormonal tablets and/or injections
- Follicular Study: Monitoring follicle size and readiness
- Sperm Preparation: Semen sample is washed and processed to extract high-quality motile sperm
- Insemination: Around Day 12–18, sperm is placed into the uterus during peak ovulation
Success Rate: Approximately 15–20% per cycle depending on individual conditions.
Precautions During IUI Treatment
- Take medications as prescribed
- Attend all scheduled scans and check-ups
- Maintain a healthy, balanced diet
- Avoid smoking, alcohol, and recreational drugs
Ovulation Induction with IUI
Combining ovulation induction with IUI can enhance results, especially for women with:
- Irregular ovulation
- Unexplained infertility
- Hormonal imbalances
Success Rate: Can reach up to 20–25% per cycle with appropriate case selection.
Benefits of IUI Treatment
- Minimally Invasive – Simpler than IVF, with no surgery required
- Natural Feel – Closely mimics natural conception
- Affordable – More budget-friendly compared to IVF or ICSI
- Quick Process – Usually done in minutes, with minimal discomfort
- Male Factor Friendly – Effective in cases of mild male infertility
- Donor Sperm Option – Available for single women or couples with male fertility issues
Risks and Considerations
While IUI is generally safe, certain side effects and rare complications may include:
- Mild Side Effects – Bloating, nausea, or water retention from fertility drugs
- Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome (OHSS) – A rare reaction causing swollen ovaries and fluid retention
- Multiple Pregnancies – Ovulation stimulation can increase the chance of twins or triplets
Important Note:
IUI requires at least one healthy fallopian tube, confirmed ovulation, and good-quality sperm. If donor sperm is used, the child’s genetic traits will come from the donor. Therefore, matching donor characteristics with the intended parents is crucial.
Without proper monitoring, ovulation induction can sometimes lead to the development of multiple follicles, causing symptoms like bloating, nausea, or constipation. In some cases, incorrect medication dosages may result in ovarian hyperstimulation. Fortunately, these risks are minimal and can be effectively managed with timely dose adjustments and close supervision.
Ovulation induction is especially effective for younger women with no additional fertility issues, offering an average success rate of 8–10% per cycle. With the right care and monitoring, it’s a safe and promising option on your path to parenthood.

Success Rate
15–25% per cycle, depending on individual conditions.

Common Use
Ideal for mild infertility, PCOS, or ovulation issues.

Treatment Duration
Typically 1–2 weeks per cycle.
