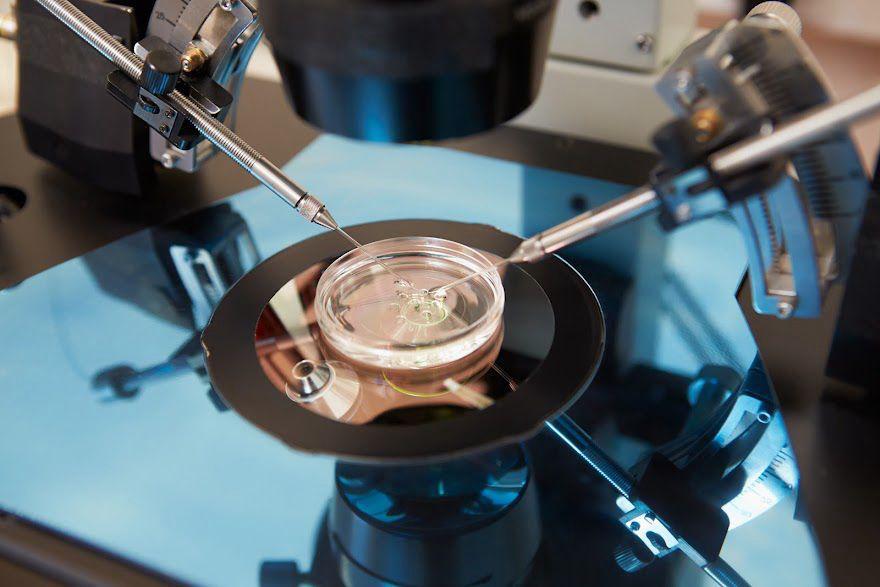
What is Laparoscopy (Keyhole Surgery)?
Laparoscopy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure used to diagnose and treat fertility-related issues. A thin tube with a camera (laparoscope) and surgical instruments are inserted through small incisions in the abdomen, allowing doctors to view and operate on reproductive organs without open surgery.
This technique is commonly used to treat endometriosis, ovarian cysts, fibroids, tubal blockages, adhesions, and other structural issues that may affect fertility.
When is Laparoscopy Recommended?
Doctors may recommend laparoscopy if you have:
- Unexplained infertility after other treatments
- Chronic pelvic pain or suspected endometriosis
- Repeated miscarriages due to uterine abnormalities
- Tubal blockages (seen in HSG scan)
- Ovarian cysts or uterine fibroids
- Pelvic inflammatory disease
- History of ectopic pregnancy
Stages of Laparoscopy Treatment
- Preparation – You’ll be under general anesthesia.
- Incision & Scope Insertion – A small cut is made in the abdomen to insert the laparoscope.
- Gas Inflation – CO₂ gas is used to inflate the abdomen for better visibility.
- Diagnosis & Treatment – The doctor examines and treats issues as needed.
- Closure & Recovery – Instruments are removed and incisions are closed.
Types of Laparoscopic Treatments
- Diagnostic Laparoscopy
- 3D Laparoscopy
- Laparoscopic Hysterectomy / Myomectomy / Cystectomy
- Hysterolaparoscopy (Hysterosalpingoscopy)
- Operative Hysteroscopy / Metroplasty / Septal Resection
- Adhesiolysis for Asherman Syndrome
- Laparoscopic Sling Surgeries
- PRP and Stem Cell Therapy
Benefits of Laparoscopy
Panacea Fertility Center provides expert laparoscopy to increase fertility chances while minimizing discomfort.
- Minimally invasive: Less pain and faster recovery
- Same-day discharge: Shorter hospital stay
- High precision: Accurate diagnosis and treatment
- Minimal scarring: Tiny incisions for better cosmetic outcomes
Possible Risks and Considerations
While generally safe, risks include:
- Mild pain or swelling at incision sites
- Infection or bleeding (rare)
- Injury to nearby organs (bladder, bowel)
- Reaction to anesthesia
- Temporary bloating due to CO₂ gas
Most patients recover smoothly with proper post-care.

Success Rate
1 to 3 days, typically with quick recovery

Common Use
Helps diagnose and treat conditions like endometriosis, fibroids, and cysts

Treatment Duration
1 to 3 days, typically with quick recovery
